Legal interoperability
Digitalisation has become a driving technological force to reckon with. Digitalisation writes code, Code sets rules. These rules compete with existing legal codes. Who is setting the scene and who knows what is cooking? In society, it is important to maintain a balance of powers based on the rule of law. Technology should be kept at bay, enabling people and business the right to choose and freedom of movement.
Some major trends in freight transport and logistics:
- Freight transport and logistics are part of the marketing mix (how to get a product or service to a place), and becoming increasingly dependent on a technology system requirements enabling seamless operations .
- Globalisation, Cost reduction and technology allowed the emphasis on transport to merge into supply chain management (and logistics).
- Extended collaboration: The different logistic operators, including government, have evolved to be interchangeable.
- From transport mode-based interaction towards platform (services) based interaction
- Focus on interoperability
- Private – borderless - platforms and conglomerates tend to take control
- Principle of democracy – minority should play a substantially part - Innovation on the edge – needs to be safeguarded.
- Urge for more state involvement to take back control
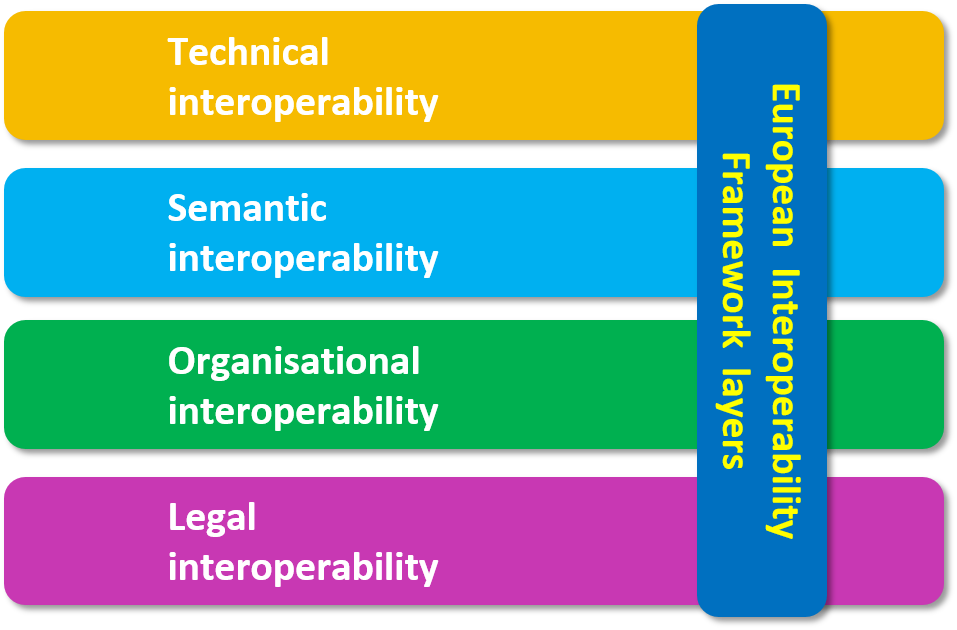
The EU Interoperability Framework is the basis of appreciation and developing insight on what to do
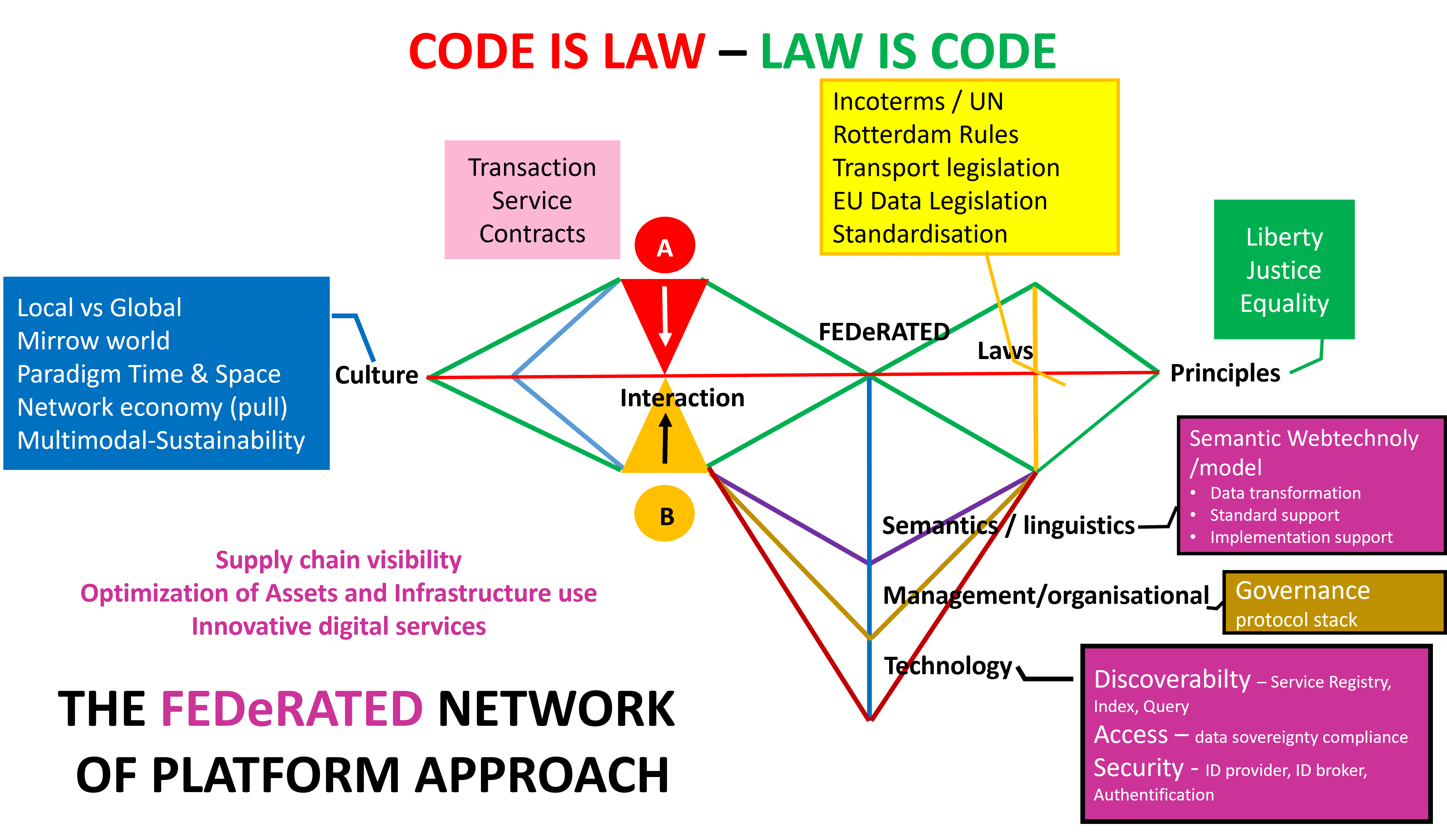
 From a legal perspective (put legal on top – take back control) some major questions are:
From a legal perspective (put legal on top – take back control) some major questions are:
- Who is writing the law?
- Who is structuring society (governing)?
- Can we maintain the Trias Politica?
- How do we effectively organize Public Private Partnerships?
The concept “Code is (evolving to become) law” is taking charge of our societies. How to countervail. Various issues can be identified:
- The Rule of Law is based on principles of justice, liberty, and equality
- Emerging governing layers (e.g., commercial platforms) can contradict the traditional Rule of Law
- Platform serving logistic operators can be uni- or multimodal
- The architecture sets the basis for the code
- Technology is the new powerhouse
- Technology defines the legal opportunity to intervene
- Code needs to be designed according to legal principles
- Singular transport mode legislation can be overruled by an overarching supply chain legal perspective
- Liability appears to be the main reason for organising a sound legal framework
Organising the network
In the EU, the aim is to develop an decentralized data-based infrastructure provision consisting of:
- Set of arrangements
- Technical applications
- Data availability
- Authorized users
- Publish and subscribe (pull) approach
To establish this network the following (EU DTLF) building blocks are identified:
- Plug and play
- Federation
- Technological independent services
- Safe, trust and secure
These building blocks translate into the FEDeRATED Core Operating Framework (COF) consisting of:
- Data quality
- Open and neutral
- Trust
- Interoperability
- Data sovereignty
The Framework constitutes the basic elements of a federated network architecture consisting of:
- Language– The ability to understand each other with minimal burdens.
- semantic model,
- data transformation,
- standard support
- implementation support
- Discoverability– the ability to discover business services and relevant data:
- Service registry – business services and data scheme’s
- Index – (dynamic) event data with links to additional data
- Search – data properties for accessing business services and finding proper event
- Accessibility – providing access to data
- Data sovereignty – owner decides on data sharing based on commercial relations
- Regulatory access – access by authorities for compliance
- Identity – using a certified identity that can be authenticated supporting OAUTH identity tokens
- Identity provider – provision of certified identity
- Authentication – authenticating an identity (token)
- Identity broker – federating different domains with certified identity providers.
- Hits: 1137